The 2018 guide to writing (and testing) real world crowdsale contracts
It's no secret - ICOs are all the rage these days. Many new companies are raising millions of dollars by selling their tokens in crowdsale. If you are reading this article, you are probably pursuing the idea of doing an ICO.
I wrote an article a few days back where I explained how one can quickly create their own tokens and sell them in an ICO. Although it offers good insights into ICO Contracts, it omits many real word aspects such as presale, public sale, discounts, security etc.
I am writing this article to demonstrate the creation of a real-world Crowdsale Smart Contract with the following improvements/characteristics:
- A Mintable ERC20 token where total supply increases as people purchase the tokens
- A refundable crowdsale with a goal and hard cap
- Presale support
- Ability to offer Presale discount
- Security
Update: I'm writing a book on Ethereum Smart Contracts. It's available for purchase on LeanPub. If you are interested in learning more about Smart Contracts and ICOs, feel free to give it a try.
Here are some of the tools we are going to use:
- node 8 & npm
- Truffle Framework
- Ganache
- Open Zeppelin
- MetaMask
The corresponding codebase is available on GitHub. Feel free to clone it and play around.
Installing Truffle
Truffle framework is the easiest way to build and test decentralized apps/contracts. I assume you already have node 8. If not, use nvm to install node 8 (with nvm you can maintain multiple node versions).
To install truffle run the following command:
npm install -g truffle
Now truffle is installed as a global node module.
Installing Ganache
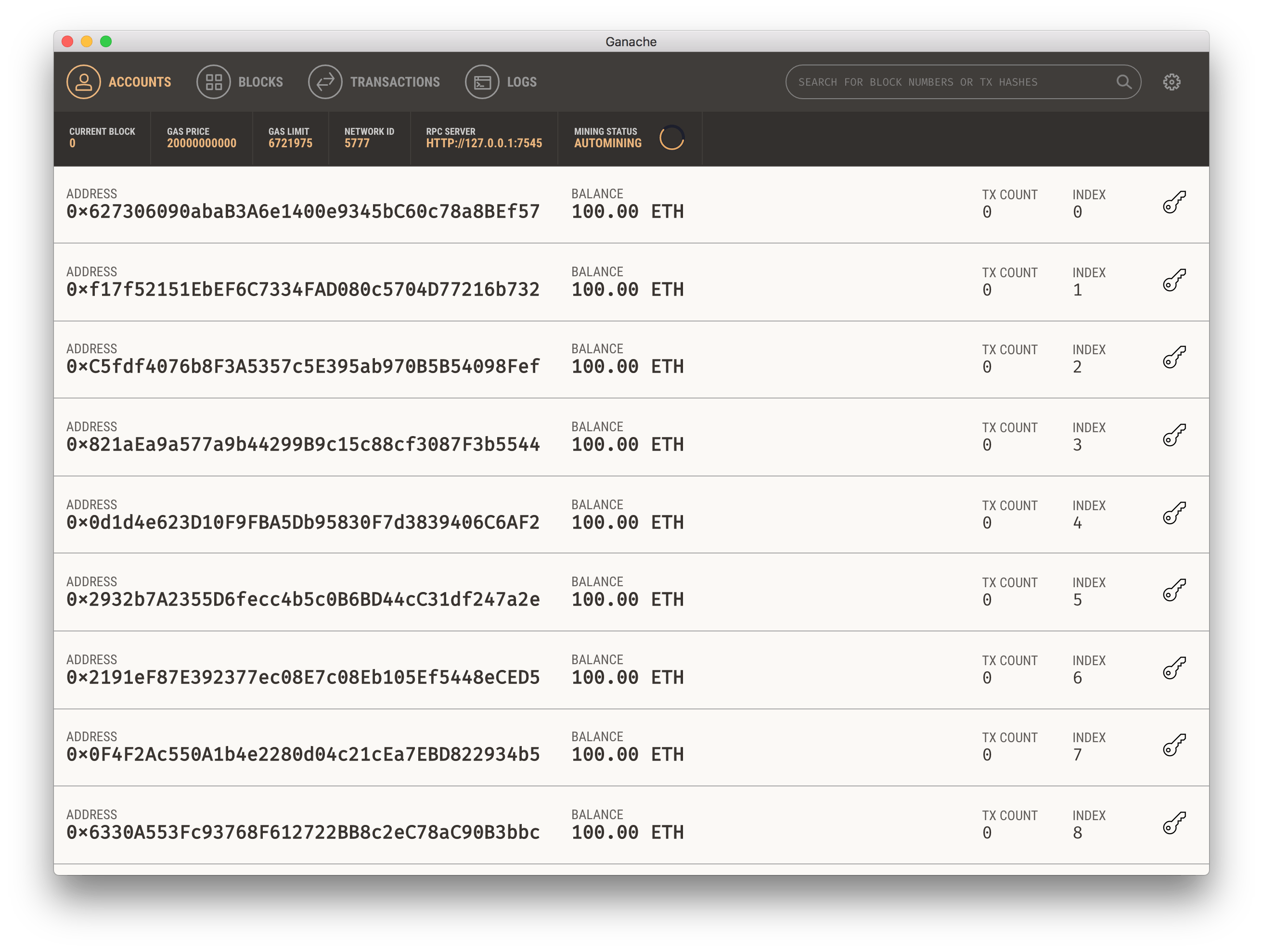
Ganache lets you run a personal Ethereum blockchain on your computer. This is where you will deploy your contracts while testing locally. Head over to Ganache website to install the latest version for your platform. Once downloaded, install the software and click on the app icon to run it.
Once started, it looks something like this:
Setting up the project
Go to your workspace and create your project directory. I am going to name it HashnodeCrowdsale:
mkdir HashnodeCrowdsale && cd HashnodeCrowdsale
Now initialize the truffle project by running the following command:
truffle init
Once the command finishes you will see the following directory structure:
HashnodeCrowdsale
contracts/
migrations/
test/
truffle.js
truffle-config.js
As the name suggests, all your Solidity source files go inside contracts/ directory. After you compile your files for the first time, you can see a build/ directory which contains all your compiled code.
Adding Open Zeppelin
You shouldn't reinvent the wheel when it comes to money. When writing Smart Contracts you should always strive to write less code. This is because less code means lesser number of bugs. Also, it is of paramount importance to write well tested and secure solidity code - you don't want to mess with people's money. 😃
Due to the above reason we'll use a library called Open Zeppelin. It has a bunch of well tested and secure Crowdsale/Token contracts. Instead of writing ERC20 tokens and Crowdsale contracts from scratch we'll use Open Zeppelin as a base contract and build upon it.
To install Open Zeppelin, run the following command:
npm install zeppelin-solidity@1.5.0
At the time of writing I am using zeppelin-solidity@1.5.0. The above command should install the zeppelin-soliditypackage inside node_modules. You can find the token & crowdsale contracts inside node_modules/zeppelin-solidity/contracts directory. We'll import these from our own solidity code.
Code
In order to launch a crowdsale we need to write our ERC20 token. So, go ahead and paste the following code into contracts/HashnodeToken.sol (you need to create this file):
HashnodeToken.sol
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import 'zeppelin-solidity/contracts/token/MintableToken.sol';
contract HashnodeToken is MintableToken {
string public name = "Hashnode Token";
string public symbol = "HT";
uint8 public decimals = 18;
}
As you may have guessed, we are just extending MintableToken provided by zeppelin-solidity package. MintableTokenitself inherits ERC20 token contract (find it inside zeppelin-solidity/contracts/token/ directory). So, the end result is that our new token HashnodeToken is an ERC20 token.
MintableToken means that the total supply of the token starts with 0 and increases as people purchase the tokens in the crowdsale. If you decide to create 100 tokens and sell 60 of them in crowdsale, the supply will increase up to 60 (as people pay ETH and buy the tokens). Once the crowdsale is over, 40 more tokens will be minted making the total supply 100.
Feel free to change the above code and supply appropriate values for name and symbol. It's recommended to set the decimals to 18 in order to be standard compliant.
Now that our ERC20 token is ready, let's proceed to code our crowdsale contract. Create the file contracts/HashnodeCrowdsale.sol and paste the following content:
HashnodeCrowdsale.sol
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import './HashnodeToken.sol';
import 'zeppelin-solidity/contracts/crowdsale/CappedCrowdsale.sol';
import 'zeppelin-solidity/contracts/crowdsale/RefundableCrowdsale.sol';
contract HashnodeCrowdsale is CappedCrowdsale, RefundableCrowdsale {
// ICO Stage
// ============
enum CrowdsaleStage { PreICO, ICO }
CrowdsaleStage public stage = CrowdsaleStage.PreICO; // By default it's Pre Sale
// =============
// Token Distribution
// =============================
uint256 public maxTokens = 100000000000000000000; // There will be total 100 Hashnode Tokens
uint256 public tokensForEcosystem = 20000000000000000000;
uint256 public tokensForTeam = 10000000000000000000;
uint256 public tokensForBounty = 10000000000000000000;
uint256 public totalTokensForSale = 60000000000000000000; // 60 HTs will be sold in Crowdsale
uint256 public totalTokensForSaleDuringPreICO = 20000000000000000000; // 20 out of 60 HTs will be sold during PreICO
// ==============================
// Amount raised in PreICO
// ==================
uint256 public totalWeiRaisedDuringPreICO;
// ===================
// Events
event EthTransferred(string text);
event EthRefunded(string text);
// Constructor
// ============
function HashnodeCrowdsale(uint256 _startTime, uint256 _endTime, uint256 _rate, address _wallet, uint256 _goal, uint256 _cap) CappedCrowdsale(_cap) FinalizableCrowdsale() RefundableCrowdsale(_goal) Crowdsale(_startTime, _endTime, _rate, _wallet) public {
require(_goal <= _cap);
}
// =============
// Token Deployment
// =================
function createTokenContract() internal returns (MintableToken) {
return new HashnodeToken(); // Deploys the ERC20 token. Automatically called when crowdsale contract is deployed
}
// ==================
// Crowdsale Stage Management
// =========================================================
// Change Crowdsale Stage. Available Options: PreICO, ICO
function setCrowdsaleStage(uint value) public onlyOwner {
CrowdsaleStage _stage;
if (uint(CrowdsaleStage.PreICO) == value) {
_stage = CrowdsaleStage.PreICO;
} else if (uint(CrowdsaleStage.ICO) == value) {
_stage = CrowdsaleStage.ICO;
}
stage = _stage;
if (stage == CrowdsaleStage.PreICO) {
setCurrentRate(5);
} else if (stage == CrowdsaleStage.ICO) {
setCurrentRate(2);
}
}
// Change the current rate
function setCurrentRate(uint256 _rate) private {
rate = _rate;
}
// ================ Stage Management Over =====================
// Token Purchase
// =========================
function () external payable {
uint256 tokensThatWillBeMintedAfterPurchase = msg.value.mul(rate);
if ((stage == CrowdsaleStage.PreICO) && (token.totalSupply() + tokensThatWillBeMintedAfterPurchase > totalTokensForSaleDuringPreICO)) {
msg.sender.transfer(msg.value); // Refund them
EthRefunded("PreICO Limit Hit");
return;
}
buyTokens(msg.sender);
if (stage == CrowdsaleStage.PreICO) {
totalWeiRaisedDuringPreICO = totalWeiRaisedDuringPreICO.add(msg.value);
}
}
function forwardFunds() internal {
if (stage == CrowdsaleStage.PreICO) {
wallet.transfer(msg.value);
EthTransferred("forwarding funds to wallet");
} else if (stage == CrowdsaleStage.ICO) {
EthTransferred("forwarding funds to refundable vault");
super.forwardFunds();
}
}
// ===========================
// Finish: Mint Extra Tokens as needed before finalizing the Crowdsale.
// ====================================================================
function finish(address _teamFund, address _ecosystemFund, address _bountyFund) public onlyOwner {
require(!isFinalized);
uint256 alreadyMinted = token.totalSupply();
require(alreadyMinted < maxTokens);
uint256 unsoldTokens = totalTokensForSale - alreadyMinted;
if (unsoldTokens > 0) {
tokensForEcosystem = tokensForEcosystem + unsoldTokens;
}
token.mint(_teamFund,tokensForTeam);
token.mint(_ecosystemFund,tokensForEcosystem);
token.mint(_bountyFund,tokensForBounty);
finalize();
}
// ===============================
// REMOVE THIS FUNCTION ONCE YOU ARE READY FOR PRODUCTION
// USEFUL FOR TESTING `finish()` FUNCTION
function hasEnded() public view returns (bool) {
return true;
}
}
The code is pretty self-explanatory and is well commented. Let me outline a few important points:
- Our crowdsale contract inherits
CappedCrowdsaleandRefundableCrowdsale(supplied byzeppelin-solidity) and therefore has a goal and a hard cap. If the contract isn't able to raise a certain minimum amount of ETH during the crowdsale, the ETH amounts will be refunded to the investors. Similarly, the contract will not be able to raise more than a specific amount of ETH due to a hard cap. - Total 100 tokens will be created by the end of the crowdsale. Out of 100, 60 will be sold in the crowdsale. Once the crowdsale is over, rest 40 tokens will be (minted and) divided among three wallets such as
teamFund,ecosystemFundandbountyFund. - The crowdsale has two stages: PreICO and ICO. You can change the stage and update
ratevariable to offer extra discounts during presale. As per the above crowdsale contract 1 ETH can buy 5 tokens in PreICO and just 2 tokens in public sale. So, the early investors get extra discounts. Note: Max 20 tokens will be sold in PreICO. - When PreICO is live, the incoming ETH amounts are immediately transferred to the beneficiary wallet (supplied while deploying the contract). However, in the public sale the raised ETH amounts are sent to a refund vault. If the crowdsale reaches its goal, the funds are transferred to the beneficiary wallet. Otherwise, investors are allowed to claim refunds (check
zeppelin-solidity/contracts/crowdsale/RefundVault.sol). - You have to call
finish()to close the crowdsale. This is where remaining tokens are minted and distributed among various reserved funds. Note: Any unsold tokens are added to the ecocystem fund.
Test and Deploy
Now that we are done coding the contract let's write a bunch of tests to make sure that everything is working as expected. So, create a new file called test/TestCrowdsale.js and paste the following:
var HashnodeCrowdsale = artifacts.require("HashnodeCrowdsale");
var HashnodeToken = artifacts.require("HashnodeToken");
contract('HashnodeCrowdsale', function(accounts) {
it('should deploy the token and store the address', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
const token = await instance.token.call();
assert(token, 'Token address couldn\'t be stored');
done();
});
});
it('should set stage to PreICO', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
await instance.setCrowdsaleStage(0);
const stage = await instance.stage.call();
assert.equal(stage.toNumber(), 0, 'The stage couldn\'t be set to PreICO');
done();
});
});
it('one ETH should buy 5 Hashnode Tokens in PreICO', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
const data = await instance.sendTransaction({ from: accounts[7], value: web3.toWei(1, "ether")});
const tokenAddress = await instance.token.call();
const hashnodeToken = HashnodeToken.at(tokenAddress);
const tokenAmount = await hashnodeToken.balanceOf(accounts[7]);
assert.equal(tokenAmount.toNumber(), 5000000000000000000, 'The sender didn\'t receive the tokens as per PreICO rate');
done();
});
});
it('should transfer the ETH to wallet immediately in Pre ICO', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
let balanceOfBeneficiary = await web3.eth.getBalance(accounts[9]);
balanceOfBeneficiary = Number(balanceOfBeneficiary.toString(10));
await instance.sendTransaction({ from: accounts[1], value: web3.toWei(2, "ether")});
let newBalanceOfBeneficiary = await web3.eth.getBalance(accounts[9]);
newBalanceOfBeneficiary = Number(newBalanceOfBeneficiary.toString(10));
assert.equal(newBalanceOfBeneficiary, balanceOfBeneficiary + 2000000000000000000, 'ETH couldn\'t be transferred to the beneficiary');
done();
});
});
it('should set variable `totalWeiRaisedDuringPreICO` correctly', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
var amount = await instance.totalWeiRaisedDuringPreICO.call();
assert.equal(amount.toNumber(), web3.toWei(3, "ether"), 'Total ETH raised in PreICO was not calculated correctly');
done();
});
});
it('should set stage to ICO', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
await instance.setCrowdsaleStage(1);
const stage = await instance.stage.call();
assert.equal(stage.toNumber(), 1, 'The stage couldn\'t be set to ICO');
done();
});
});
it('one ETH should buy 2 Hashnode Tokens in ICO', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
const data = await instance.sendTransaction({ from: accounts[2], value: web3.toWei(1.5, "ether")});
const tokenAddress = await instance.token.call();
const hashnodeToken = HashnodeToken.at(tokenAddress);
const tokenAmount = await hashnodeToken.balanceOf(accounts[2]);
assert.equal(tokenAmount.toNumber(), 3000000000000000000, 'The sender didn\'t receive the tokens as per ICO rate');
done();
});
});
it('should transfer the raised ETH to RefundVault during ICO', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
var vaultAddress = await instance.vault.call();
let balance = await web3.eth.getBalance(vaultAddress);
assert.equal(balance.toNumber(), 1500000000000000000, 'ETH couldn\'t be transferred to the vault');
done();
});
});
it('Vault balance should be added to our wallet once ICO is over', function(done){
HashnodeCrowdsale.deployed().then(async function(instance) {
let balanceOfBeneficiary = await web3.eth.getBalance(accounts[9]);
balanceOfBeneficiary = balanceOfBeneficiary.toNumber();
var vaultAddress = await instance.vault.call();
let vaultBalance = await web3.eth.getBalance(vaultAddress);
await instance.finish(accounts[0], accounts[1], accounts[2]);
let newBalanceOfBeneficiary = await web3.eth.getBalance(accounts[9]);
newBalanceOfBeneficiary = newBalanceOfBeneficiary.toNumber();
assert.equal(newBalanceOfBeneficiary, balanceOfBeneficiary + vaultBalance.toNumber(), 'Vault balance couldn\'t be sent to the wallet');
done();
});
});
});
Each it() block introduces a scenario and performs some actions on the contract to verify that the code is behaving as expected. I have written total 9 test cases. Feel free to think of more scenarios and write the corresponding tests.
Before running the tests we need to tell truffle that we have introduced a new contract called HashnodeCrowdsale. Create a new file migrations/2_HashnodeCrowdsale.js with the following content:
var HashnodeCrowdsale = artifacts.require("./HashnodeCrowdsale.sol");
module.exports = function(deployer) {
const startTime = Math.round((new Date(Date.now() - 86400000).getTime())/1000); // Yesterday
const endTime = Math.round((new Date().getTime() + (86400000 * 20))/1000); // Today + 20 days
deployer.deploy(HashnodeCrowdsale,
startTime,
endTime,
5,
"0x5AEDA56215b167893e80B4fE645BA6d5Bab767DE", // Replace this wallet address with the last one (10th account) from Ganache UI. This will be treated as the beneficiary address.
2000000000000000000, // 2 ETH
500000000000000000000 // 500 ETH
);
};
Now open up zeppelin-solidity/contracts/crowdsale/Crowdsale.sol and comment out line number 44 where it says:
require(_startTime >= now);
We need to do the above modification so that we can set crowdsale start date to yesterday while deploying. Otherwise you have to provide a future date as the crowdsale start date which will be difficult to test.
The above code keeps our contract ready for deployment with the following settings:
- startTime is yesterday
- endTime is startTime + 20 days
- Current rate is 5 i.e. 1 ETH can buy 5 HTs
- 0x5AEDA56215b167893e80B4fE645BA6d5Bab767DE is the beneficiary wallet. You should replace this with the 10th wallet address (usually the last one) from Ganache UI. If you choose a different wallet from ganache, the last test case will fail! (Can you find out the reason? 😉 )
- Goal is 2 ETH and hard cap is 500 ETH
Now go to truffle.js and paste the following:
module.exports = {
networks: {
development: {
host: "localhost",
port: 7545,
gas: 6500000,
network_id: "5777"
}
},
solc: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200
}
}
};
Ganache (installed earlier) is running on port 7545. The above code configures the local blockchain (Ganache) details and registers with truffle.
Now it's time to compile, deploy and test our code.
truffle compile
truffle migrate // deploy to local blockchain (Ganache)
To test, run the following command:
truffle test
Do note that truffle test command automatically compiles and deploys your contracts before running the tests.
If the tests are successful, you should see something like this:
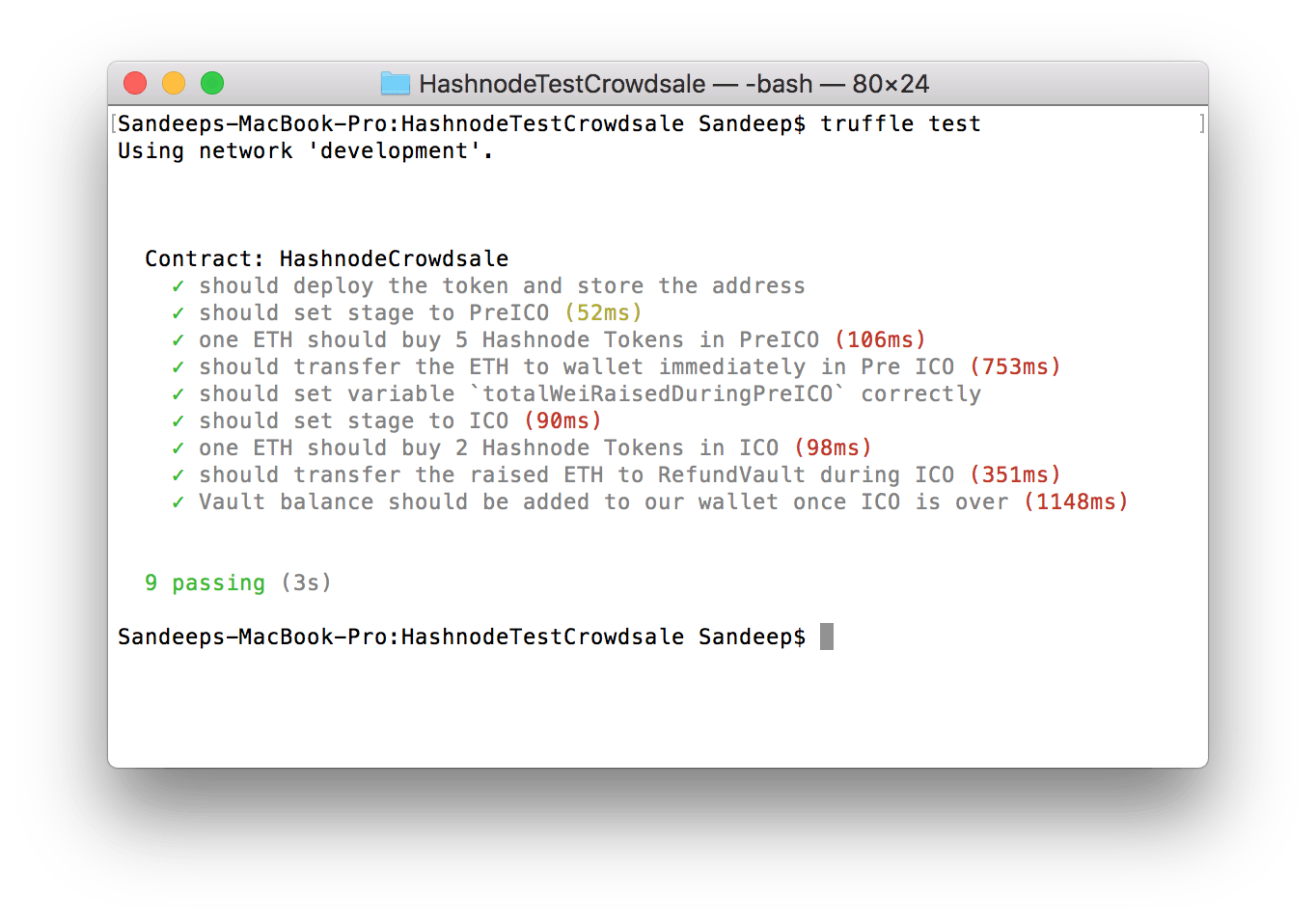
Congrats! You have verified your contract on your local machine.
Deploy to Ropsten TestNet
Now let's go one step ahead and deploy our code to Ropsten TestNet. In order to do that we need an ethereum wallet. For the sake of simplicity let's use MetaMask (also my personal favorite). So, go ahead and download the extension for your browser. Currently, it's available for Chrome, Firefox, Opera and Brave.
Once you have installed MetaMask, choose a password and note down the 12 word seed phrase.
Also, buy some test Ether by clicking on "Buy" button in MetaMask. It'll take you to a faucet where you can request some test ETH. We'll need this to pay our transaction fees while deploying the contract.
Now go ahead and paste the following code into truffle.js:
var HDWalletProvider = require("truffle-hdwallet-provider");
var infura_apikey = "KbQuP7xkP1ZYNhJkUOXF"; // Either use this key or get yours at infura.io/signup. It's free.
var mnemonic = "<REPLACE THIS WITH YOUR METAMASK SEED PHRASES>";
module.exports = {
networks: {
development: {
host: "localhost",
port: 7545,
gas: 6500000,
network_id: "5777"
},
ropsten: {
provider: new HDWalletProvider(mnemonic, "ropsten.infura.io" + infura_apikey),
network_id: 3,
gas: 4500000
}
},
solc: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200
}
}
};
Replace the variable mnemonic with the seed phrases obtained from MetaMask and run npm install. We did this so that truffle chooses the first account created on MetaMask to deploy the contract.
If everything was installed correctly, run the following command to deploy your contract to Ropsten TestNet:
truffle migrate --network ropsten
It will take some time for the deployment to complete. Once it's over, you will see something like this:
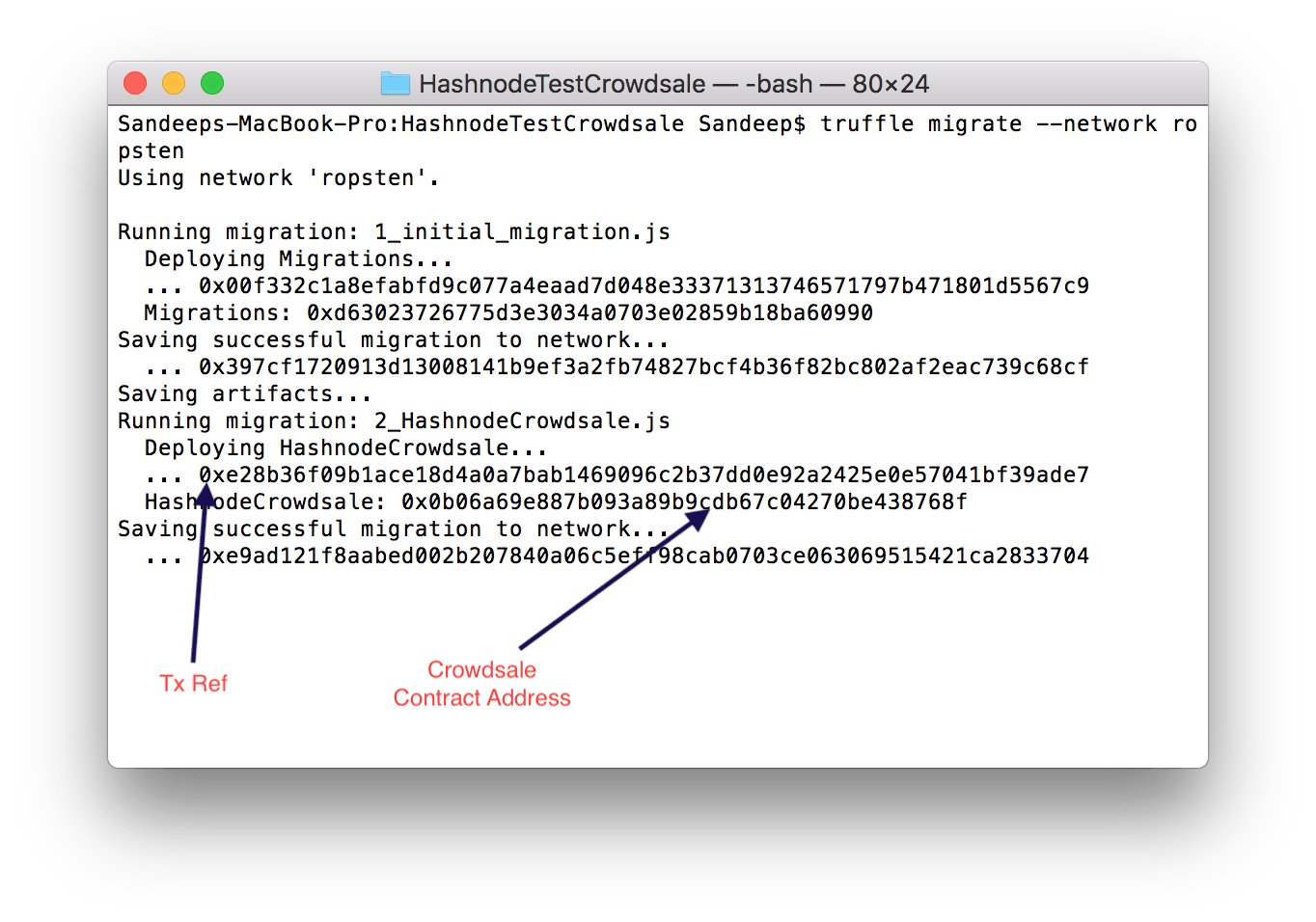
Congrats! Your crowdsale is now live on TestNet. Note the contract address and Tx ref.
Testing
You can go ahead and test all the 9 scenarios on Ropsten. But for the sake of brevity, let's conclude this article with just 1 test which is: If I send 1 ETH to the Crowdsale Contract, I should get back 5 HTs.
So, open up MetaMask and send 1 ETH to the contract address. Once the transaction is complete (you can check the status on Etherscan), go to the tokens tab of MetaMask.
MetaMask doesn't show all your tokens by default. You have to add the specific token in order to see your balance. At this time we just have the crowdsale contract address. So, how do you get the ERC20 token address?
If you look at the contract code, you will see that there is a public variable token defined in zeppelin-solidity/contracts/crowdsale/Crowdsale.sol';. This is the address of your ERC20 token.
So, how do we read its value? It's simple. As the contract HashnodeCrowdsale automatically deploys HashnodeToken, you can find its address from the internal transactions tab on Etherscan.
Go to the following address:
https://ropsten.etherscan.io/tx/<txRef>#internal
Replace txRef with the Tx Ref we noted earlier. Once the page loads click on the "To" address of the first row. It'll take you to a new page where you can see the Contract Address.
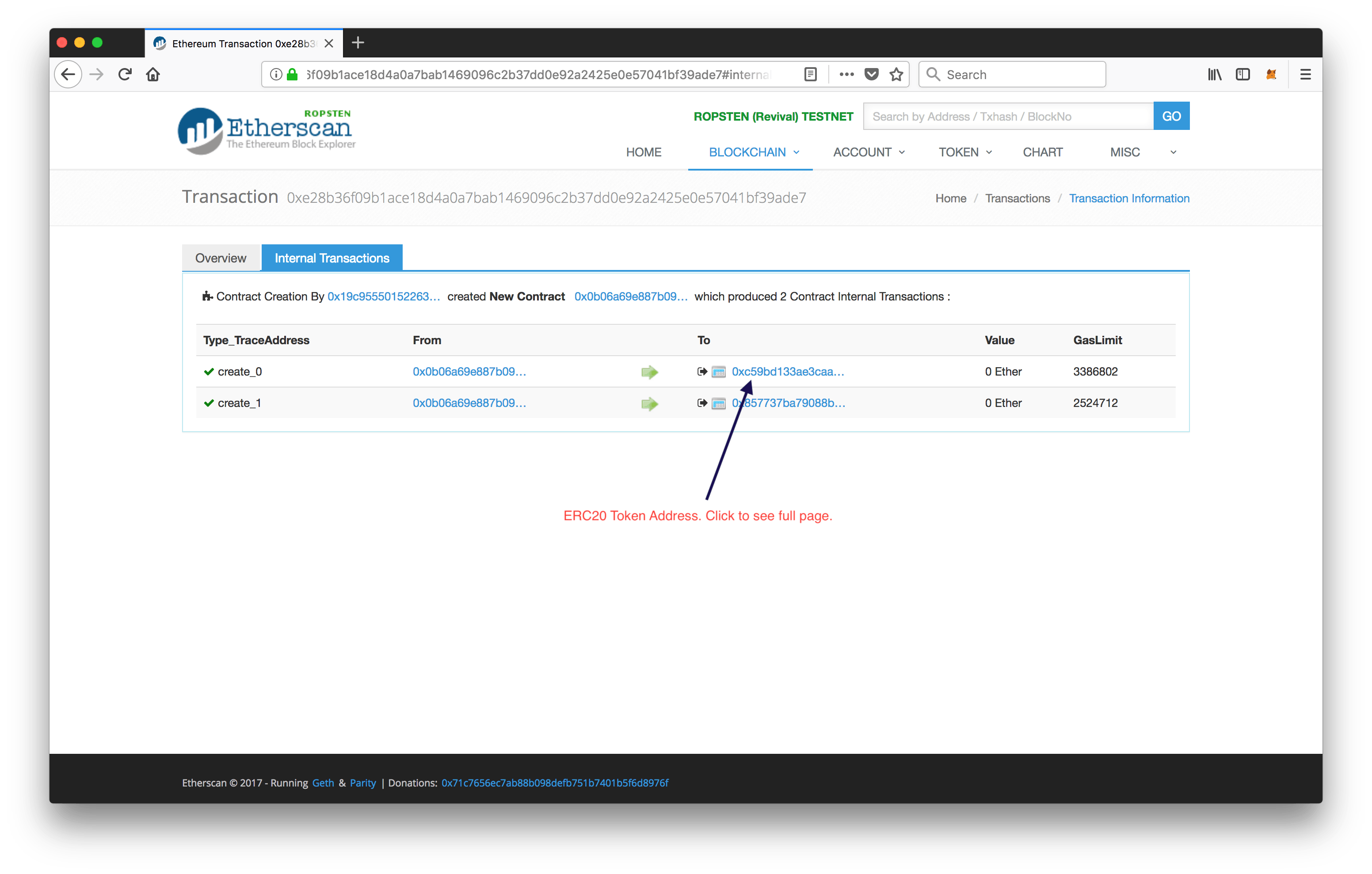
Note the address. Now go to MetaMask -> Tokens -> Add Token. Paste the token address. The symbol and decimals will be populated automatically. Hit Add and you are done!

If everything worked correctly, you should see 5 HTs in your account. In case you don't see it immediately after adding the token, refresh MetaMask. Sometimes MetaMask UI doesn't update after adding a new token.
Feel free to check all possible scenarios and let me know your findings in the comment section!
ICO Demo & Conclusion
I quickly put together some code to build a simple ICO page. Do check it out and read the source code to understand how to interact with your Smart Contracts through JavaScript.
If you spot any errors or inaccuracies, please report them in the comments - and as always feel free to ask any questions. Happy to help!